Mole fraction describes the number of molecules of one component divided by total the number of molecules in the mixture. Mole fraction is useful when two reactive components are mixed together, as the ratio of the two components is known if the mole fraction of each is known. Multiplying mole fraction by 100 gives mole percent, which describes the same thing as mole fraction, just in a different form. Mole fractions can be generated from various concentrations including molality, molarity and mass percent compositions. Noting that the atomic mass of hydrogen is 1 amu and that of oxygen is 16 amu, the molar mass of acetone is 58 grams.
That means the total number of moles in solution is 1.84. Now you're ready to calculate mole fractions using the mole fraction equation. Mole fraction and mass fraction are used to express the relative fractions of different constituents in a mixture. Both are unit-less terms since the ratios have the same unit, and thus the units cancel out. Mole fraction is a measure of concentration of a chemical solution.
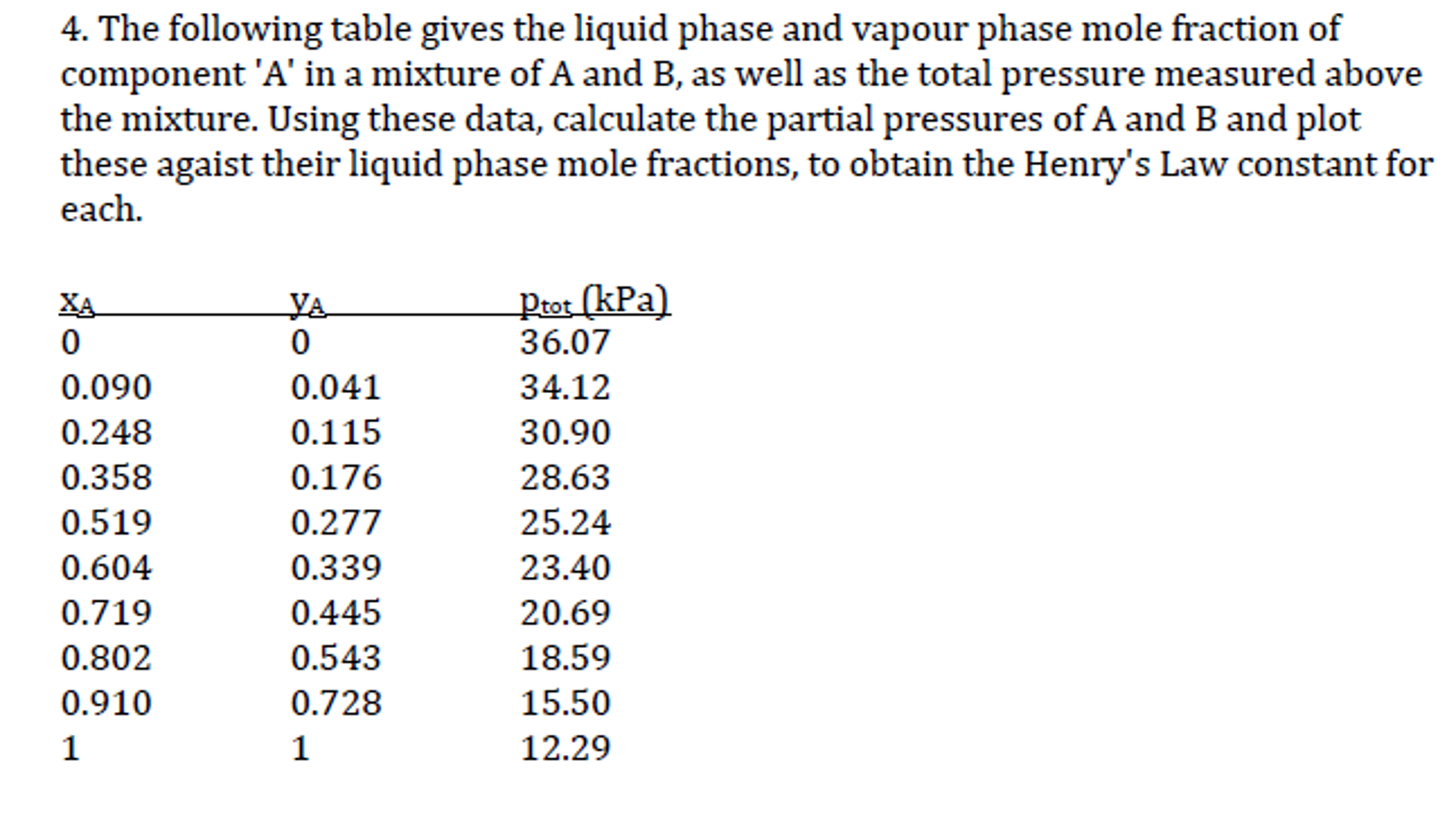
It can be calculated by dividing the number of moles of one component of a solution by the total number of moles of all components of the solution. The sum of mole fractions of all components in the solution is always equal to 1. Chemical reactions are always balanced using moles of the reactant and the product.
The concentration of a solution involves the mole of a solute. Some examples are molar concentration or molarity, molality, mole fraction, molar density. The mole fraction is another way of expressing the concentration. Mole fraction is the number of moles of a component divided by the total number of moles.
The symbol for mole fraction is the capital letter X or the lowercase Greek letter chi (χ). The terms "amount fraction" or "amount-of-substance fraction" mean the same as mole fraction. The mass fractions of all components is equal to 1 since the mass fraction is a ratio.
The mass fractions of individual components are always lower values than 1. In elemental analysis calculations, mass fraction refers to the ratio between the mass of a chemical element and the compound. The mass fraction is independent of temperature because mass does not change when the temperature is changed.
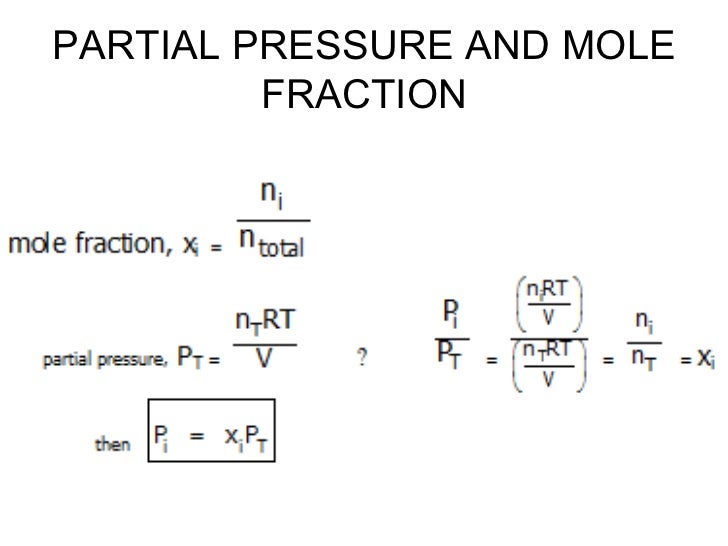
Finding the mole fraction of a particular constituent of a solution is useful for a number of reasons. Using the definition of a mole, it is possible to calculate several other figures based on the mole fraction. In a mixture of ideal gases or most real gases, the mole fraction is the same as the ratio of partial pressure of a gas to the total pressure of the mixture.
In other words, mole fraction follows Dalton's law of partial pressure. When analyzing solutions, chemists measure concentrations of components in moles. The mole fraction of a solute is the ratio of the number of moles of that solute to the total number of moles of solute and solvent in solution. Because it's a ratio of moles to moles, the mole fraction is a dimensionless number, and of course, it's always less than one. Therefore, we can say that Mole Fraction equation is the ratio of the reactant substances that react/combine to form a product. The mole ratios calculator is the best way to calculate mole fraction instantly.
One of the primary components of an LNAPL site conceptual model is characterization of LNAPL chemistry , often including the mole fractions of individual constituents. Mole fractions are important because they help in predicting constituent (e.g., benzene) concentrations in groundwater and soil gas that contact the LNAPL. Also, decreasing mole fractions over time are an indication of source zone depletion. The mole fractions of all components equals 1 since the mole fraction is a ratio. The mole fraction can be used to express the mole percentage by multiplying the mole fraction from 100.
The mole fraction can also be called the amount fraction because moles give the amount of a constituent. Mole fraction is unit-less since it is a ratio between moles . Molality is the moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. Using these units, you can calculate mole fraction if you know molality. For example, find the mole fraction of table sugar or sucrose in a 1.62 m solution of sucrose in water.
To calculate mole fraction of solute you first calculate the moles of the solute and then you divide that by the total number of moles of solute and solvent. In a mixture of ideal gases, the mole fraction can be expressed as the ratio of partial pressure to total pressure of the mixture. We use the total pressure of the gas in Equation 4.18 and not the partial pressure because we are using the volume fraction based on the total volume and total pressure of our system.
If we used the total volume of the system instead of the volume fraction, then we would use the partial pressure of the gas and Equation 4.18 would look something like Equation 4.21. One major benefit of the behavior of gases is that the volume of one ideal gas in a mixture of ideal gases is equivalent to its mole fraction. For all practical purposes, the volume fractions and the mole fractions of the components of an ideal gas mixture are interchangeable. For example, let's calculate the mole fraction of solute A in a solution composed of 2 moles of solute A and 4 moles of solvent B. For the above example, an estimated molecular weight is 259 g/mole. For the laboratory-reported 20 mg/kg benzene and 15,000 mg/kg TPH concentrations in soil, the corresponding benzene mole fraction in LNAPL would be 4.4 x 10-3 mole/mole.
Mole fraction and mass fraction are terms used to express the ratios between different components in compounds. Mole fraction can be converted into the mass fraction of the same compound and vice versa. Here, the amount of CCl4 is already in moles, but you can't find mole fraction until you convert grams of CH2O into moles, too. Look up the atomic masses of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen on the periodic table and use the chemical formula for formaldehyde to calculate the number of moles.
The Average Molecular Weight of a mixture is computed from the molar composition and the molecular weight. It is a weighted average-- the molecular weights are averaged using the mole fractions as weights. Often, you will be given a composition in percent or fraction form, but to solve the problem you will need to know the masses of the individual components . Take care of this by assuming abasis of 1 kg, 100 mol, etc. and work from there.
After all, if a mixture is 21 mole percent oxygen, it doesn't make a difference if you've got 5 g or 30 lb or 200 mol -- the percentage or fractional composition is the same. Using the mole ratios calculator is helpful while calculating it online. Reactants take a part in the chemical reaction and reactants are the substances which are combined with each other to make new substance or products. Reactants has its own impact on the chemical reaction therefore it becomes important to calculate the actual value of reactants. The mole fraction to mass fraction calculator can be very useful in this context.
Just like the mole fractions, the partial pressures should add up to the total pressure. For the laboratory-reported benzene content of 200 mg/kg in the LNAPL sample, and calculated 177 g/mole molecular weight, the corresponding benzene mole fraction is 4.5 x 10-4 mole/mole. Mole fraction represents the mulber of molecules of a particular component in a mixture divided by the total number of moles in the mixture.
Its a way of expressing concentration of a chemical solution. Therefore, the sum of mole fraction of all component should be equal to 1. To calculate the mole fraction from molarity, first multiply the molarity by the volume followed by dividing the product by a thousand. This applies to both solvent and the solution if their mole concentration is available in terms of molarity. First, we assume a total mass of 100.0 g, although any mass could be assumed.
This means that we have 50.0 g of urea and 50.0 g of cinnamic acid. We can then calculate the moles present by dividing each by its molecular weight. We have 0.833 moles urea and 0.388 moles cinnamic acid, so we have 1.22 moles total. We must first find the number of moles present in 10.0 g of each component, given their chemical formulas and molecular weights. The number of moles for each is found by dividing its mass by its respective molecular weight. We find that there are 0.138 moles of pentane, 0.116 moles of hexane, and 0.128 moles of benzene.
The partial pressure of a gas is the pressure that the gas would have if it was in the container all by itself. It can be calculated if you know the total pressure and the mole fraction of the gas concerned. A lot of times, the terms "composition" and "concentration" are used interchangeably. At this point, we want to make clear the difference.Concentration is based on volume and is one way of expressing composition. The mass concentration is the mass of a component per unit volume, similarly molar concentration is the moles per unit volume.
By dividing the moles of each reactant with the moles of all reactants, you can calculate the Molar Fraction of respective reactants. This page explains equilibrium constants expressed in terms of partial pressures of gases, Kp. It covers an explanation of the terms mole fraction and partial pressure, and looks at Kp for both homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions involving gases. A 12.5 L tank is filled with helix mixture containing 24.2 g of He and 4.32 g of O2 at 298 K. Calculate the mole fraction, partial pressures of each gas, and the total pressure in the tank.
Molecular weights for LNAPLs can vary by a factor of 2 or 3, so it is worth obtaining an estimate of this value for a given sample. One estimation method is based on the carbon distribution of the LNAPL, obtained from a simulated distillation analysis (e.g., ASTM D3710). In a simulated distillation, the LNAPL is boiled at sequentially higher temperatures that are referenced to known chemical standards, typically aliphatic hydrocarbons (Villalanti et al. 2000). An example laboratory that performs simulated distillation and reports carbon numbers as mass fractions is Energy Laboratories .
The MWi term is a known value based on the molecular formula of the constituent. A "mole" is actually a number of molecules, approximately 6×1023. A "mole fraction" is the ratio of molecules of one component in a mixture.
For example, if the mole fraction of methane in natural gas is 0.90, then this means that 90% of the molecules are methane. Since the volume fractions are equivalent to mole fractions, the mixture is also 90%, by, methane. 1 through C6, have discrete values, while the concentrations of others, the unidentifiable components such as C7+, are described as a continuous distribution function, F. A solution contains 25% water, 25% ethyl alcohol and 50% acetic acid by mass calculate the mole fraction of each component.
How To Find Mole Chemistry A mole is defined as the number of molecules present in 12 grams of pure carbon-12. This number, also known as Avogadro's number, is 6.02 x 1023. A mole of any substance is contains this same number of molecules.
This means that a mole of any substance has a mass of the combined atomic numbers of all the atoms present in one molecule of that material, in grams. This is useful in writing chemical equations and for other calculations in chemistry. Students can learn about both if they refer to Mole Fraction – Definition, Formula, Properties, and Solved Examples on our e-learning platform. Some advantages of mole fractions are that they have never been dependent on temperature, to calculate a mole fraction, it is not important to find out information about the density of the phase. If you go through this page on Mole Fraction, all your doubts will be taken care of in the best possible manner. Questions on their advantages and disadvantages have a probability of coming for tests.
In the text below, we will explore the details of the mole fraction formula, calculate the mole fraction of gas, and transform mole fraction to molality. Mole fraction is another way of expressing the concentration of a solution or mixture. It is equal to the moles of one component divided by the total moles in the solution or mixture. Chemical reactions, when molecules interact to create new substances, can be written as equations. Learn more about the basic properties of chemical reactions and chemical equilibrium. Kp has exactly the same format as Kc, except that partial pressures are used instead of concentrations.
The gases on the right-hand side of the chemical equation are at the top of the expression, and those on the left at the bottom. We can also find the number of moles of each gas by conversion. Make sure that your units match the idea gas constant, R. The mole fraction is a way to express the composition of a mixture.
Other quantities are molarity, molality, mass fraction. Mole Fraction The mole fraction of a component substance A in a solution is defined as the moles of component substance divided by the total moles of solution . Mole fraction is a unit of concentration, defined to be equal to the number of moles of a component divided by the total number of moles of a solution. Because it is a ratio, mole fraction is a unitless expression.
The mole fraction of all components of a solution, when added together, will equal 1. Mixing binary mixtures with a common component gives a ternary mixture with certain mixing ratios between the three components. We are using yi for the mole fraction of a gas so as to be consistent with the nomenclature used later in this text where we will use xi for the mole fraction of component i in a liquid. It is the molarity because you can see that we calculated everything in terms of 997 gm which is equal to 1000ml or 1 L. As we know molarity is moles of solute in 1 litre of solution.
Q. What are the mole fractions of H3PO4 and water in a solution of 14.5 g of H3PO4 in 125 g of water? Mole fraction calculator uses mole fraction formula to work. You just have to place the number of moles of the substances, respectively as per the given directions. As Mole Fraction is the ratio of the reactants, having the values of the moles of the reactants known, you can evaluate the concentration of each reactant involved in a chemical reaction. In turn, having the value of the concentration of the substances known can help you in analyzing and balancing the chemical reactions properly. A) Mole Fraction - it is defined as the ratio of number of moles of one component to the total number of moles of solute & solvent present in the solution.